Confocal Microscopy: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
====Code==== | ====Code==== | ||
* Here is an Arduino sketch to read the | |||
output voltage of the photodiode detectors. | output voltage of the photodiode detectors. | ||
The output pin of the circuit is connected | The output pin of the circuit is connected | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
However, you can change the sampling | However, you can change the sampling | ||
rate by simply changing the argument of the | rate by simply changing the argument of the | ||
delay() statement. * | delay() statement. * | ||
#define inPin0 0 | #define inPin0 0 | ||
void setup(void) { | |||
void setup(void) { | |||
Serial.begin(9600); | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
Serial.println(); | Serial.println(); | ||
} | } | ||
void loop(void) { | void loop(void) { | ||
float pinRead0 = analogRead(inPin0); | float pinRead0 = analogRead(inPin0); | ||
| Line 58: | Line 57: | ||
/* the minimum delay allowed is about 20, correspond | /* the minimum delay allowed is about 20, correspond | ||
is about 20ms */} | is about 20ms */} | ||
delay(25); | delay(25); | ||
} | |||
} | |||
==Experimental process== | ==Experimental process== | ||
Revision as of 08:21, 29 April 2022
Introduction
A Confocal Microscopy is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph. It uses pinhole to block out all out of focus light to enhance optical resolution, very different from traditional wide-field fluorescence microscopes. To offset the block of out of focus lights, the light intensity is detected by a photomultiplier tube or avalanche photodiode, which transforms the light signal into an electrical one. We will try to build a Setup like this to enhance optical resolution and maybe get profile information about the sample.
Team Members
Wang Tingyu, Xue Rui, Yang Hengxing
Principles of confocal microscopy
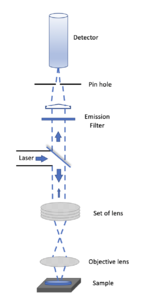
The method of image formation in a confocal microscope is fundamentally different from that in a conventional fluorescence microscope , where the entire specimen is subjected to intense illumination from an incoherent lamp, and resulting image of secondary fluorescence emission can be viewed directly by eye or detector. This usually requires a thin, relatively transparent, sample but often results in out-of-focus blur that reduces resolution and specimen contrast. In contrast, the illumination in a confocal microscope is achieved by scanning focused beam from laser and across the specimen.
The confocal principle is diagrammatically presented in Figure 1. Coherent light emitted by the laser system (excitation source) pass through a low-pass filter that is situated in a conjugate plane (confocal) with a scanning point on the specimen and a pinhole aperture positioned in front of the detector (Si PIN photodiode). As the laser is reflected by a dichromatic mirror and scanned across the specimen in a defined focal plane, secondary fluorescence emitted from points on the specimen pass back through the dichromatic mirror and are focused as a confocal point at the pinhole aperture.
Set up
The confocal fluorescence microscope consists of multiple laser excitation sources, a scan head with optical and electronic components, electronic detector (Si PIN photodiode), and a computer for acquisition, processing, analysis, and display of images.
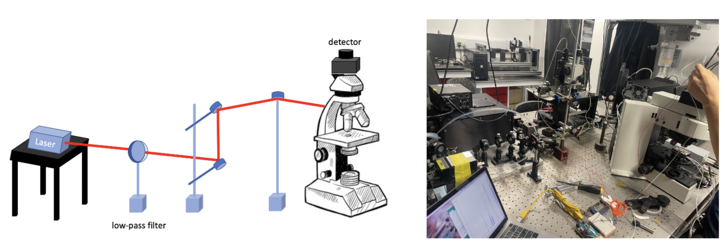
Laser
Si PIN photodiode

High-speed Si PIN photodiodes are designed for visible to near infrared light detection for they can efficiently convert light into an electrical current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in the photodiode. These photodiodes provide wide-band characteristics at a low bias, making them suitable for optical communications. In this project, we choose S5973 series with a mini-lens type (S5973-01) that can be efficiently coupled with an optical fiber and a violet sensitivity enhanced type (S5973-02) ideal for violet laser detection.
XYZ piezo scanner
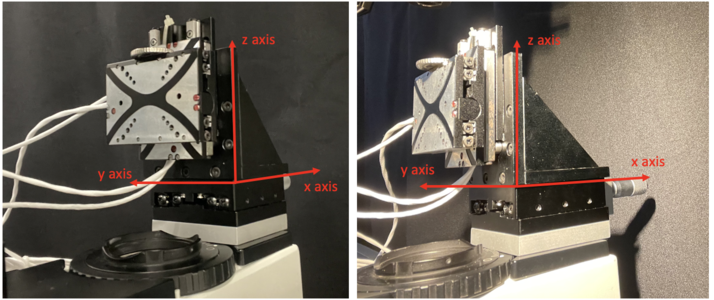
Piezo scanners are used for fast, high precision motion in one or more axes. In our project, we combine the micro PI stage controller with a moving stage on x-axis to realise three dimensional piezo scanning in our confocal microscopy.
Arduino UNO
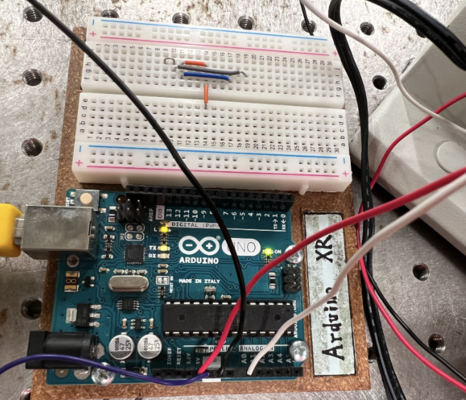
Code
- Here is an Arduino sketch to read the
output voltage of the photodiode detectors.
The output pin of the circuit is connected
to analog pin 0 of the Arduino. The data are
read every 0.025 second in this example.
However, you can change the sampling
rate by simply changing the argument of the
delay() statement. *
#define inPin0 0
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println();
}
void loop(void) {
float pinRead0 = analogRead(inPin0);
Serial.println(pinRead0);
/* the minimum delay allowed is about 20, correspond
is about 20ms */}
delay(25);
}
Experimental process
Laser calibration
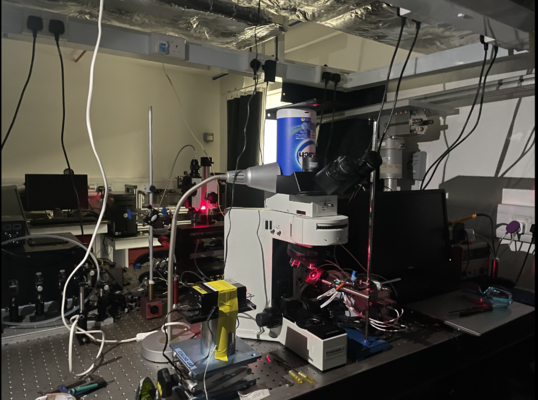
To realise the focus both on the focal plane of specimen and pinhole aperture, we built the set up shown in Figure.6. After the adjustment, we fix the height of the x-y scanner and detector.
Lab Location
S12-01-10/11 Nanomaterials Research Lab