Argon gas discharge lamp: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Glass Pipe=== | ===Glass Pipe=== | ||
===Vacuum Components=== | ===Vacuum Components=== | ||
==High-Voltage Power Supply=== | ===High-Voltage Power Supply=== | ||
===High-Voltage Probe=== | ===High-Voltage Probe=== | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 27 April 2022
By applying a sufficiently high DC voltage across a gas, the gas atoms/molecules are ionised by the strong electric field. In this project, we construct an Argon-based gas discharge lamp, with adjustable pressure and voltage. The breakdown voltage of Argon gas with respect to pressure changes is observed, and compared with Paschen's law. We also observe changes in the spectroscopic properties of the plasma with varying pressure.
Setup
A small air-tight chamber was evacuated with a rough pump to about Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 3\times10^{-3}} Torr (measured with a Pirani gauge). Then, Argon gas was slowly introduced to the chamber via a needle valve, until the chamber reached the pressure of about Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 10^{-1}} to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 10^0} Torr. The metallic cylinder that interfaces with the gas lines forms the cathode of the chamber, and is grounded. Another metallic cylinder (anode) was attached to the cathode using a glass pipe.
The glass pipe provides an electrical isolation between the cathode and the anode, and provides a viewport for the experimenter to observe glow discharge. The anode was connected to the positive terminal of a high-voltage power supply, which can reach upto 760 V. Epoxy was used to connect the pieces and seal the vacuum chamber. A ballast resistor (33 kΩ) was added in series with the gas discharge lamp in order to limit the current. The electrodes were mechanically held using laser-cut acrylic plates fixed to an optical breadboard using brackets and bolts. Multimeters were used to monitor the current and the voltage across the lamp.
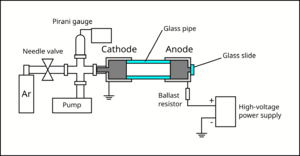
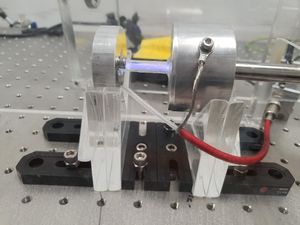
Electrodes
Glass Pipe
Vacuum Components
High-Voltage Power Supply
High-Voltage Probe
Breakdown Voltage
The ions and free electrons produced from a sufficiently high voltage (above breakdown voltage) move towards the respective electrodes, and current is formed across the lamp. The moving charges collide with other particles to multiply the number of charge carriers in the gas. This process is known as Townsend avalanche. The excited atoms and ions decay to the ground state and emit light, in the form of glow discharge.