Plasmaspec: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
: ☑ High-voltage DC source: using 300 VDC for now | : ☑ High-voltage DC source: using 300 VDC for now | ||
: ☐ Resistor | : ☐ Resistor | ||
[[File:Plasma-schematics.png|720px|Schematics for Argon plasma diagnostics]] | |||
==Measurements== | ==Measurements== | ||
Revision as of 16:17, 10 February 2022
Pulsed plasma in partial vacuum is characterised, by analysing line intensity ratios to determine its temperature and density. The following can be explored:
- Passive spectroscopy
- Active absorption spectroscopy with a laser
- Measuring plasma frequency
- EM wave propagation in plasma
Team members
- Park Kun Hee
- Yang Jincheng
- Qin Jingwen
(Reach us if you want to join.)
Idea
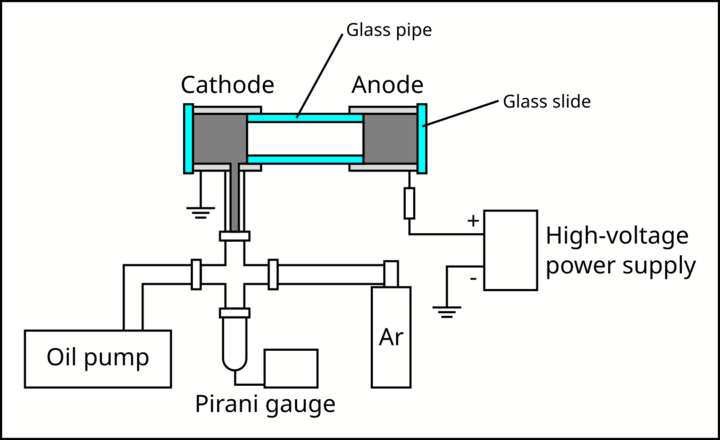
In this project, a quiescent Argon plasma is produced in a vacuum by a high-voltage DC source. A spectrometer is used to obtain spectral line ratios of different transitions, through a view port. Dependence of plasma characteristics (temperature, density, frequency, etc.) on parameters such as voltage and pressure is explored.
Setup
- Logistics
- ☐ Vacuum pump and vacuum parts
- ☐ Pirani gauge
- ☐ Can of Argon gas
- ☐ Electrodes
- ☐ Thermometer: to measure the temperature of the cathode
- ☐ Glass tube and glass slides
- ☑ High-voltage DC source: using 300 VDC for now
- ☐ Resistor